or
or is a logic primitive that takes two conditional statements and reports true if either is true. In other words, it will report true if 1) the first condition is true but the second is false, 2) the second condition is true but the first is false, or 3) both conditions are true. or will report false only if both of the conditions are false. For example, if we wanted to create a model of a predator-prey ecosystem where deer only move if there was no grass nearby or if there was a wolf nearby, we would write the following code:
ask deer [
if grass-here = 0 or any? wolves in-radius 2 [
move
]
]
Things to keep in mind when using or:
- We can string together multiple
orstatements if we want to check more than just two conditions such asif color = red or size < 2 or [ ... ]. In such a statement, if only just one of the statements reportstrue, the whole statement will reporttrue. andis a primitive that does the exact opposite ofor; it reportstrueonly if both conditions are true.- If we need to check if either condition is true, but not at the same time, we can use the
xorprimitive.
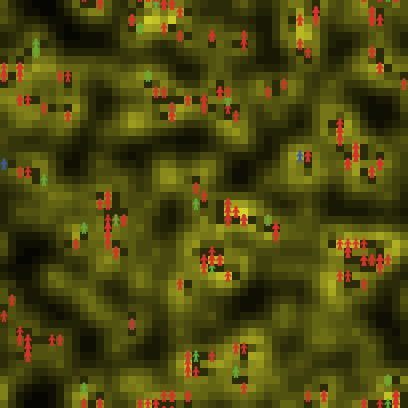
In the model example below, we have some plants and some sheep. Sheep move around randomly and they eat a plant if it is either green or yellow. A magenta plant indicates a poisonous one, so sheep don't eat.
Try it Yourself
What's next?
Once you mastered the or primitive, don't stop there. Check out the resources below to improve your NetLogo skills.
Published NetLogo models that use the or primitive:
Similar primitives:
if
Carries out a provided set of rules (code) if a given condition is true. Does nothing if a given condition is false.