all?
all? checks if all agents of an agentset satisfy one or more true-false conditions. If all the agents satisfy the given condition, all? itself will report true. If even one of the agents in the given agentset fail to satisfy the condition, all? will report false.
For example, all? turtles [ size > 1 ] would report true if and only if every turtle in the model were larger than one unit.
Things to keep in mind when using all?:
- Don't forget the question mark (
?) at the end. - You should encapsulate your conditionals within square brackets
[...]. - You can combine multiple conditional statements using the
andprimitive. all?itself does not do anything; you should use it within a conditional statement such asifandif-elseor other primitives that require true-false values such aswhile.
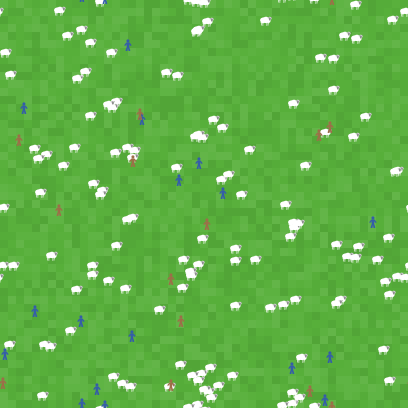
In the model example below, there is a flock of sheep. The sheep move around randomly and once they are on a green patch, they eat the grass on that patch. We want the model to stop after all sheep have eaten at least once, so we include the following line:
if all? turtles [ food-eaten > 0 ][
stop
]
Try it Yourself
What's next?
Once you mastered the all? primitive, don't stop there. Check out the resources below to improve your NetLogo skills.