max-pycor
max-pycor reports the pycor of the topmost patches in a model. This primitive, and its siblings min-pxcor, max-pxcor, min-pycor, are very useful in modeling the agent behavior that involves the boundaries of an environment. For example, if we wanted to build a model where we had a wall at the edges, we would write the following code:
ask patches [
if pxcor = max-pxcor or
pxcor = min-pxcor or
pycor = max-pycor or
pycor = min-pycor [
set pcolor gray
]
]
Or if we wanted turtles to not walk beyond the world's borders, we would write the following code:
ask turtles [
if [pxcor] of patch-ahead 1 < max-pycor [
forward 1
]
]
Things to keep in mind when using max-pycor:
max-pxcor,min-pxcor,max-pycor, andmin-pycorare not variables; they are constant reporters. That is, a code such asset max-pycor 30would show an error message.- You can change your model's size through the Settings button in the Interface Tab or using the
resize-worldprimitive.
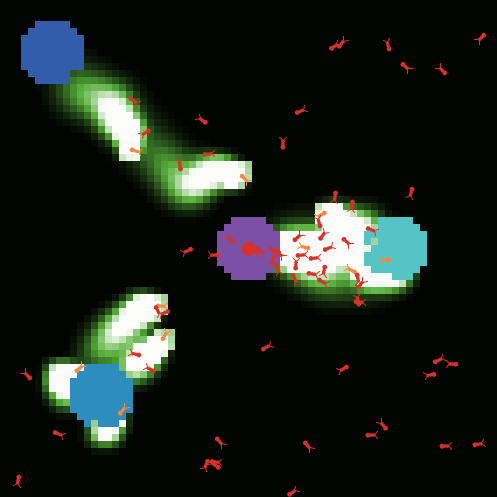
In the model example below, we use max-pycor and its siblings to create walls that represent a container. The balls inside the container bounce off of the green wall but they stick to the red wall.
Try it Yourself
What's next?
Once you mastered the max-pycor primitive, don't stop there. Check out the resources below to improve your NetLogo skills.